Anahtar Kelimeler:DeepSeek, OpenAI, Google Android XR, Zhiyuan Robot, Doubao Telefon Asistanı, AI Öğrenme Ortağı, SpaceX Yörünge Veri Merkezi, DeepSeek R1 Modeli, OpenAI Kırmızı Alarm, Android XR SDK, Zhiyuan Robot Expedition A1, Doubao AI Asistanı Çapraz Uygulama İşlemi
🔥 Spotlight
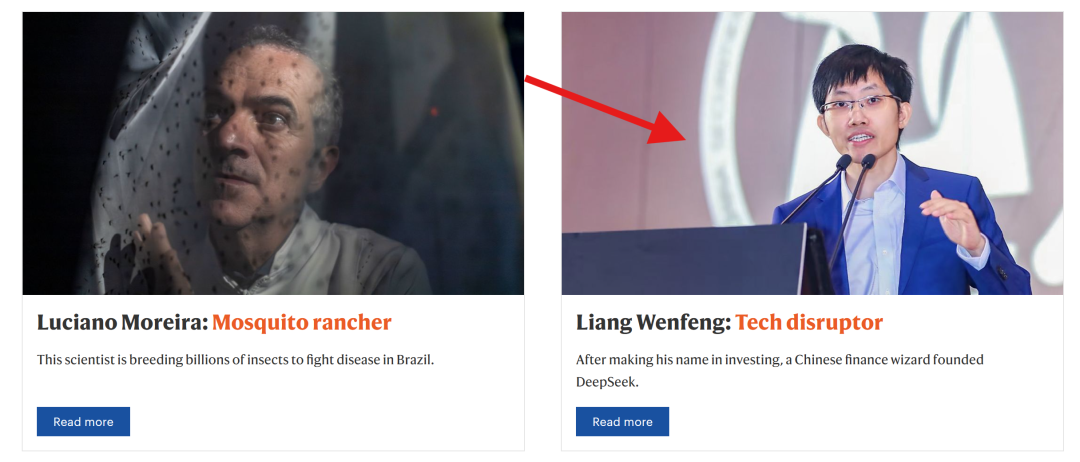
DeepSeek Founder Liang Wenfeng Named One of Nature’s Ten People of the Year: Liang Wenfeng was recognized by Nature magazine as one of its Ten People of the Year for 2025 due to DeepSeek models’ contributions and transformative impact in the AI field, earning him the title “tech disruptor.” DeepSeek disrupted the industry with its powerful, cost-effective, and open-source models (such as R1, V3.2), proving that large models don’t necessarily require unlimited resources to achieve top-tier performance, thereby boosting the technical influence of domestic large models in the global community. DeepSeek’s valuation has reached 1.05 trillion yuan, and Liang Wenfeng’s net worth has surged to 184.62 billion yuan. His “geek” persona and commitment to open source are seen as a symbol of China’s AI transition from imitator to innovator. (Source: 36氪, 36氪, 36氪)
OpenAI Issues “Red Alert” and Releases Enterprise AI Report: OpenAI CEO Altman issued a “red alert” on December 1st, the highest level, due to fierce competition from Google Gemini and Meta, pausing non-core businesses to focus resources on strengthening ChatGPT’s core advantages. Concurrently, OpenAI released its “State of Enterprise AI Report,” indicating an accelerated adoption rate of enterprise AI, with employees saving nearly an hour of work time daily on average. However, the top 5% of power users saw their efficiency surge by 16 times, raising concerns about an “AI era wealth gap.” The competition focuses on model capabilities, market share, and talent acquisition. (Source: 36氪, 36氪)
Google Unveils Android XR Platform and Multiple AI Glasses: During its XR Edition event, Google systematically showcased Android XR, positioning it as the first unified extended reality platform designed to extend the Android experience into the XR domain. The platform, in collaboration with Samsung and Qualcomm, introduces diverse hardware forms, including stylish AI smart glasses (in partnership with Warby Parker, Gentle Monster), wired XR glasses (Project Aura with XREAL), and updates to the Samsung Galaxy XR headset. The Android XR SDK was also updated concurrently, providing full support for developers and signaling significant progress in the integration of AI and XR. (Source: 36氪, 36氪)

Zhiyuan Robotics, Founded by Zhihui Jun, Achieves Mass Production of 5,000 Robots: Zhiyuan Robotics, founded by embodied AI entrepreneur “Zhihui Jun” Peng Zhihui, has achieved mass production of 5,000 general-purpose embodied robots in less than three years. Its product line includes full-size humanoid robots (Expedition A1/A2), half-size humanoid robots (Lingxi X1/X2), and wheeled embodied robots (Elf G1/G2), primarily applied in industrial manufacturing, logistics sorting, data collection and training, as well as reception, entertainment, and commercial performances. This milestone indicates that the mass production progress in the embodied AI industry has exceeded expectations, with orders worth hundreds of millions of yuan already secured. (Source: 36氪)

Doubao Mobile Assistant Ignites Battle for AI Era Entry Point: ByteDance’s Doubao Mobile Assistant, through deep collaboration with ZTE, attempts to embed AI capabilities into the mobile operating system layer to enable cross-application global operations, causing industry ripples. The product aims to challenge the traffic entry point status of existing super apps but immediately encountered technical restrictions from major players like WeChat and Taobao. This incident brings the competition for super entry points in the AI era to the forefront, indicating that software-hardware integration, ecosystem accumulation, and edge-cloud collaboration will be key trends for future AI assistant development. (Source: 36氪, 36氪)

🎯 Trends
AI Veteran Zou Yang: AGI Not Core, Application Deployment Changes the World: Zou Yang, co-founder of Future Intelligence, believes that while current large language model technology has not yet reached AGI, it is already sufficient to thoroughly transform various industries. He emphasizes that the true value of AI lies in integrating into industrial processes, becoming an “external brain” for repetitive intellectual work in enterprises, and enabling the structured replication of expert knowledge. He points out that the industry should focus on how to embed existing technologies into business operations and achieve large-scale implementation, rather than excessively pursuing the distant peak of AGI. (Source: 36氪)

AI-Generated Advertising Reshapes Industry, Opportunities and Challenges Coexist: Artificial intelligence is profoundly reshaping the digital advertising industry, evolving from programmatic to intelligent advertising systems. Opportunities include diversified traffic entry points, automated content generation, extreme personalization (“one person, a thousand faces”), intelligent delivery mechanisms, and the transformation of advertising agency roles. However, challenges such as insufficient technological maturity (unstable model inference, inexplicable algorithms), regulatory hurdles (false advertising, deepfakes), user trust and privacy risks, and cross-border compliance costs urgently need to be addressed. The industry needs to build a “light regulation + co-governance” system, upgrade platform risk control, strengthen data governance, and encourage brands to build their own intelligent agents. (Source: 36氪)
Global Insurance Outlook 2026: AI Reshaping the Rules of the Game: A Deloitte report indicates that the global insurance industry is entering deep waters of slowing growth and profit pressure, with AI becoming a key force in reshaping industry rules. In the non-life insurance sector, AI achieves “predictive risk” through actuarial science, fraud detection, and risk early warning; in life and annuity insurance, changes in capital structure and accelerated integration of private equity make asset management capabilities central; in group insurance, under the B2B2C model, digital access capabilities and ultimate user experience are key competitive advantages. Large-scale AI application relies on high-quality data, modern systems, and security guarantees, and requires professionals to undergo skill transformation. (Source: 36氪)

Google’s New HOPE Architecture Addresses Large Model Long-Term Memory Challenge: Google proposed the new HOPE framework in a paper, aiming to solve the long-term memory problem in large models, which is crucial for the widespread application of AI agents. This architecture defines Transformer’s self-attention mechanism as a “short-term system” and introduces an independent neural long-term memory module responsible for storing and recalling key information across context windows, redefining the “brain structure” of large models. Long-term memory is evolving from an engineering patch into a core model capability, determining whether AI can be used and trusted over the long term. (Source: 36氪)

AI Learning Partners Reshape Education, Integrating Skill, Emotional, and Knowledge Companionship: AI learning partners are rapidly emerging in the global education sector, embedding themselves into students’ daily learning as “companions.” In skill training, AI language tutors (e.g., Duolingo Roleplay, Gulu Oral English) offer immersive conversations and instant error correction. For psychological companionship and habit management, AI (e.g., Replika, Xueersi “Xiao Si 3.0”) provides emotional support and habit guidance. In knowledge guidance, AI (e.g., PhotoMath, Xiaoyuan AI Hyper-realistic Teacher) is evolving towards “one-on-one full-subject tutoring,” offering process-oriented explanations. (Source: 36氪)
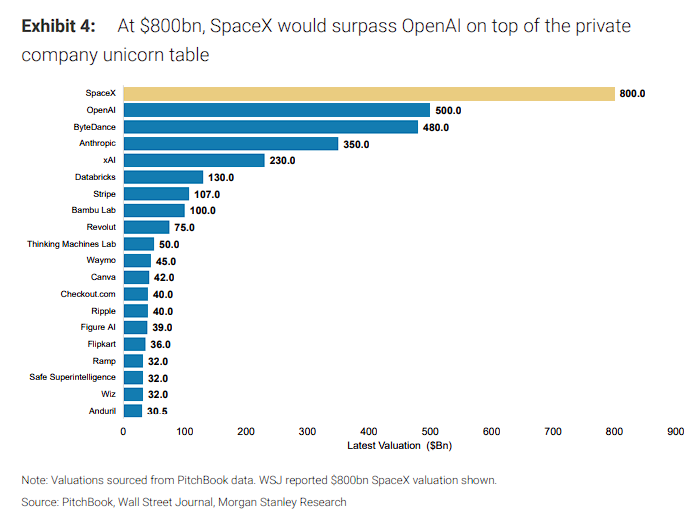
Musk’s Grand Narrative: SpaceX Ventures into Orbital Data Centers: A Morgan Stanley report indicates that SpaceX’s soaring valuation is partly due to the market pricing in the grand narrative of “orbital data centers” as a new AI infrastructure. Musk envisions using Starship and Starlink V3 satellites equipped with GPUs to form a massive computational cloud in orbit via high-speed laser interconnects, addressing Earth’s power shortages, achieving extreme cooling, infinite energy, and global edge connectivity. This field has attracted numerous players, including Starcloud, Axiom Space, Google, and NVIDIA. (Source: 36氪)
🧰 Tools
Zhipu AI Open-Sources Multimodal Large Model GLM-4.6V Series: Powerful Features, Half the Price: Zhipu AI has open-sourced its GLM-4.6V series multimodal large models and AutoGLM agents, aiming to lower the entry barrier for multimodal AI. GLM-4.6V increases the context window to 128k tokens and natively integrates Function Call into a vision model for the first time. Practical tests show stable performance in image-based shopping, webpage replication, long document, and video understanding, though text-image layout still needs optimization. Its API price has been halved, and the lightweight GLM-4.6V-Flash version is free, promoting the application of multimodal AI among individuals and small teams. (Source: 36氪)
AI Learning Partners Reshape Education, Integrating Skill, Emotional, and Knowledge Companionship: AI learning partners are rapidly emerging in the global education sector, embedding themselves into students’ daily learning as “companions.” In skill training, AI language tutors (e.g., Duolingo Roleplay, Gulu Oral English) offer immersive conversations and instant error correction. For psychological companionship and habit management, AI (e.g., Replika, Xueersi “Xiao Si 3.0”) provides emotional support and habit guidance. In knowledge guidance, AI (e.g., PhotoMath, Xiaoyuan AI Hyper-realistic Teacher) is evolving towards “one-on-one full-subject tutoring,” offering process-oriented explanations. (Source: 36氪)

📚 Learning
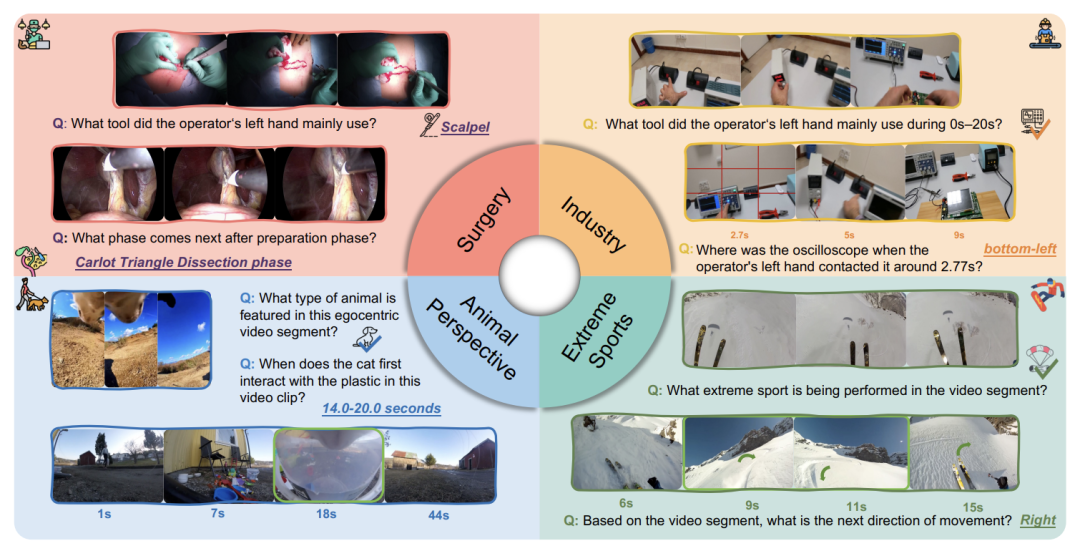
Large Model Vision Capabilities “Fail”: EgoCross Reveals Cross-Domain Generalization Bottleneck: The EgoCross project team focused on cross-domain first-person video question answering evaluation, revealing the generalization bottleneck of existing MLLMs in specialized scenarios such as surgical operations, industrial settings, extreme sports, and animal perspectives. The study found that even top models saw their accuracy plummet to below 55% in these unfamiliar domains, far lower than in everyday scenarios. The team built the first cross-domain EgocentricQA benchmark and, through methods like prompt learning, supervised fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, verified that RL methods can bring significant performance improvements, providing direction for building more generalizable models. (Source: 36氪)
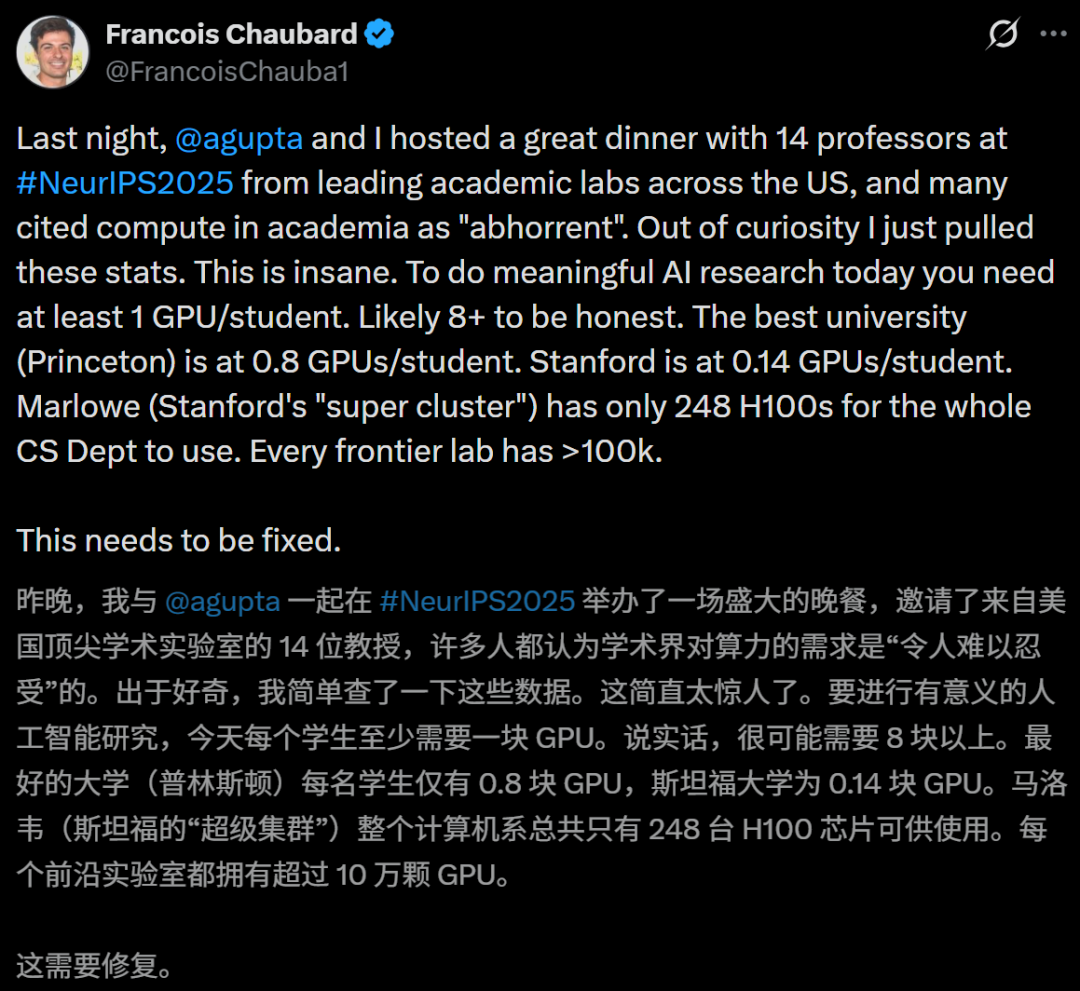
Academia’s Computing Power “Slaughtered”: Stanford Averages ≈0.1 GPUs Per Person: Leading university labs in the U.S. are widely facing severe GPU shortages, with Stanford, for instance, having only about 0.14 GPUs per person, far below the industry average. This makes it difficult for academia to conduct large-scale AI research, accelerates the exodus of top talent to industry, and gradually diminishes academia’s ability to define the frontier. Although some universities (e.g., NYU, UT Austin) are building their own AI factories, the overall resource gap remains vast, posing a severe challenge to AI research and education. (Source: 36氪)
Human-Robot Interaction and Social Robotics: An Interview with Professor Marynel Vasquez: The AAAI podcast “Generations in Dialogue” interviewed Professor Marynel Vázquez to discuss human-robot interaction (HRI) and social robotics research. Professor Vázquez’s research focuses on social group dynamics in multi-party environments, developing perception and decision-making algorithms that enable autonomous, socially aware robot behaviors, and modeling interactions as graphs to allow robots to simultaneously reason about individuals, relationships, and groups. She also discussed the potential of robots in education and how to address societal misconceptions about robots. (Source: aihub.org)

💼 Business
AI Simulation Startup Aaru Secures 350 Million Yuan Funding, Valuation Exceeds $1 Billion: U.S. AI synthetic research startup Aaru, founded by three post-05 generation founders (the youngest being 16), reportedly completed over $50 million (approximately 350 million yuan) in Series A funding, reaching a nominal valuation of $1 billion. Aaru’s core technology uses AI Agents to simulate human behavior and predict specific demographic responses to events. It has been successfully applied in political election polling and provides data model products for enterprises, political circles, and public sectors. (Source: 36氪)

Former OpenAI Researcher Teams Up with Google to Encircle NVIDIA: A fund established by former OpenAI researcher Leopold Aschenbrenner is reportedly in talks to lead a Series A funding round of over $700 million for cloud service provider Fluidstack. Fluidstack, serving as a Google TPU distribution channel, aims to challenge NVIDIA’s computing power monopoly. This move highlights Google’s strategic layout in the AI chip sector and the capital market’s fervent pursuit of AI infrastructure. (Source: 36氪)

Shenzhen AI Companion Robot Company Enabot Secures Sequoia Investment, User Base Exceeds One Million: Enabot (Fuzhi Technology), with its AI companion robot products, has surpassed one million global users and secured multiple rounds of funding from investors including Sequoia and Longfor Capital. The company initially entered the pet companionship market but later unexpectedly discovered the vast market for human emotional companionship. It then integrated AI large model dialogue and multimodal emotional interaction technologies to launch home robot products like EBO X. Product functions range from remote monitoring and interaction to emotional resonance, adapting to user needs across different cultural backgrounds. (Source: 36氪)

🌟 Community
AI Glasses Face “Last Mile” Challenge in Offline Adoption: Despite the high online popularity of AI glasses, their offline adoption in Guangzhou’s core business districts is far below expectations. The market faces a “dual identity” challenge: traditional optical stores lack tech knowledge, while digital stores don’t offer professional eyeglass fitting services. The challenge of fitting prescription lenses for AI glasses with displays (e.g., Rokid’s magnetic attachment solution and Quark S1’s high-cost integrated solution) also limits their widespread adoption. The report suggests that for AI glasses to truly enter mainstream life, an offline system must be established that allows consumers to “buy with confidence, fit easily, and use smoothly.” (Source: 36氪)

Tesla Robot’s “Remote-Controlled Fall” Sparks Debate, Autonomy Questioned: Tesla’s Optimus robot reportedly fell after seemingly being remote-controlled to “remove its headset” during an event, sparking widespread social media discussion and questioning the robot’s autonomy. Previously, Optimus was also reported to have used robotic arm assistance for folding clothes and to have its movements remote-controlled by engineers behind the scenes. Despite Musk’s high hopes for Optimus, these incidents highlight the challenges of fully autonomous intelligence for humanoid robots and have sparked discussions about the value of remote-controlled robots and future work models. (Source: 36氪)

Conversing with Models in the AI Era: Amanda Askell Shares Her Methodology: Amanda Askell, a Philosophy PhD at Anthropic and known as Claude’s “personality designer,” shared her methodology for establishing collaborative relationships with AI models. She likens AI to a “forgetful genius,” emphasizing that conversing with models requires clearly expressing intentions, breaking down complex tasks, and providing sufficient context. She shapes Claude’s personality through “soul documents,” making it gentle and boundary-aware. She believes that ordinary people should shift from “writing commands” to “designing conversations,” and enterprises should view AI as an employee rather than a tool, with personalized AI becoming a key differentiator for products. (Source: 36氪)
China’s AI Startup Scene “Aging”: Market Prefers Experience and Resources: Observations reveal that at Chinese AI startup DemoDays, founders are generally older (mostly post-80s, pre-95s), and products exhibit a “middle-aged aesthetic,” such as smart hearing aids and industrial embodied AI. This contrasts with the “youthful storm” of AI startups in the U.S. Analysis suggests that AI application-layer startups in China require deep customer understanding, strong product-market fit, and accumulated resources. These “time-dependent issues” make “youth” a disadvantage. Concurrently, the oligopolization of large models and the demand for “large and beautiful” applications are prompting more experienced executives from major companies to venture into entrepreneurship, making the “aging of the AI startup scene” a trend. (Source: 36氪)

Amazon Employees Jointly Resist AI Strategy, Fearing It Will “Destroy Democracy, Jobs, and the Planet”: Over 1,000 Amazon employees have co-signed an open letter, warning that the company’s “out-of-control” pace of AI advancement could cause immense harm to democracy, jobs, and the planet. Employees are concerned that Amazon is sacrificing climate commitments for AI (increased data center carbon emissions), accelerating job displacement (mass layoffs, mandatory AI integration), and expanding surveillance technology (police access to Ring cameras). They call on Amazon to publish a renewable energy plan, establish mechanisms for employee involvement in AI decision-making, and commit that AI technology will not be used for violence, surveillance, or mass displacement. Amazon denies the allegations. (Source: 36氪)

Attribution of Liability for AI Agent Damages: Adaptation and Adjustment of Existing Legal Frameworks: The legal community is discussing the issue of liability attribution for AI agent damages, debating whether a completely new legal framework is needed or if existing laws (such as negligence and product liability) can be adapted. Some argue that AI agents are similar to traditional products, and developers and users should bear responsibility based on their ability to prevent risks. The challenge lies in AI’s complexity, unpredictability, and opacity, which make proving negligence and causation difficult. It is suggested that existing laws be carefully adjusted, for example, by imposing stricter accountability on developers and enhancing the technological literacy of legal professionals, to ensure a reasonable allocation of responsibility. (Source: 36氪)